With the market for cloud solutions growing faster than my cat’s current need to topple my Christmas tree down, most companies are now using some kind of cloud business solution somewhere in their organization.
And for good reason!
Today, cloud computing accounts for a hefty 33% of IT budgets worldwide. A considerable glow up from past data storage technology, the cloud lets businesses access applications from anywhere, decreases data loss with regular backups to other servers, and saves companies considerable money on server maintenance by using remote resources, among other things.
WHICH CLOUD SERVICE IS RIGHT FOR ME?
So you’ve decided to migrate to the cloud! That’s great! You even have an idea of some of the cloud computing technologies out there (hint: we highlighted the top five cloud computing technologies here to help you get started). Even better! But how do you know which one is right for you and your business needs?
That is the question.
Thankfully, we’re here to arm you with the information you need to make your decision a little easier.
In the first of this three-part series on cloud computing technology, we will cover an introduction to one of the most popular and well-known cloud computing platforms: Microsoft Azure.
Sit back, grab a cup of coffee, and get ready to dive into all things Azure!
AN INTRODUCTION TO MICROSOFT AZURE
Are you one of those people who’ve heard the buzzword “Microsoft Azure Cloud”, and landed here to see what the heck that term actually means? Don’t worry, you’ve reached the right place. And if you stumbled here by accident, stick around! We promise you’ll learn something you might not know you needed or wanted to.
As you probably already know, you can take advantage of cloud computing services that offer rapid, reliable, remote, and on-demand computing power for cheap. They help with costs, scalability, and security, among a whole host of other things.
Many companies offer cloud services, including Microsoft’s cloud service, Azure.
Azure is a cloud computing platform created by Microsoft that developers and IT professionals use to build, deploy, and manage applications through their global data centers.
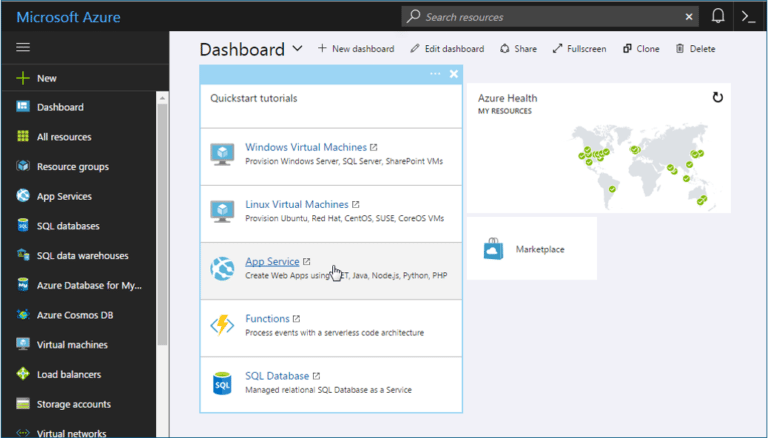
Suppose you check out the Microsoft Azure website. You’ll be blessed with a directory chock full of hundreds of different services you can use, including complete virtual machines, databases, file storage, backups, and services for mobile and web apps.
Digging through these hundreds of services, you’ll see that you can do practically anything. And for anything Azure doesn’t offer, you can set up a Windows or Linux virtual machine that hosts whatever software you want to use.
What’s even more impressive is that Azure is one of the most popular cloud services in the world. In fact, over 95% of Fortune 500 companies use it. It’s more affordable than Amazon Web Services (AWS) and provides a robust marketplace of trusted third-party applications.
We see you, Azure. We see you.
WHAT DOES AZURE DO?
Now that you know a little more about what Azure is, let’s chat quickly about what it does, which is, quite frankly, a lot.
The Azure platform provides over 600 (that’s right, 600!!) specific services to its users, including but not limited to:
- Basic Web Services
- Running Virtualized Computers
- Remote Storage
- Database Hosting
- Centralized Account Management
- Intelligent Bots
- Mixed Reality
- Machine Learning
Sheeeeeesh! That’s pretty incredible.
However, it’s important to note that the infrastructure on Azure isn’t just a bunch of services like the ones we mentioned above. You need to understand the basic pillars: compute, network, and storage.
Everything on Azure is built on top of those pillars, and they form a foundation for your cloud infrastructure too. You can build your own architecture from infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) products, such as Azure Virtual Networks, Azure VMs, Azure VDI, and Azure Disc Storage. Or you can take advantage of the platform-as-a-service (PaaS) offerings, such as Azure SQL and Azure app services. All are built on top of the pillars, but offer different layers to build your business applications.
Whatever your computing needs are, Azure can help.